- Home
- Common Knee Conditions
- Bursitis
- Suprapatellar Bursitis
Suprapatellar Bursitis
Written By: Chloe Wilson, BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed by: KPE Medical Review Board
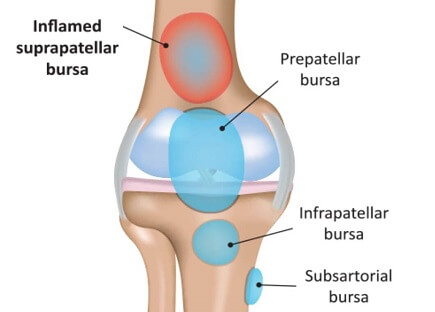
Suprapatellar bursitis is a common cause of pain and swelling just above the knee joint.
Also known as quadriceps tendon bursitis, suprapatellar bursitis develops when there is inflammation and irritation of one of the small fluid-filled sacs at the knee.
This may be from repetitive overuse in sports, frequent kneeling, an injury or an underlying medical condition and causes pain, swelling and reduced knee movement.
But with the right treatment, most cases of suprapatellar bursitis will settle down within a few weeks. Here we look at the common causes and symptoms, how it is diagnosed, suprapatellar bursitis treatment options and the recovery process.
What Is Suprapatellar Bursitis?
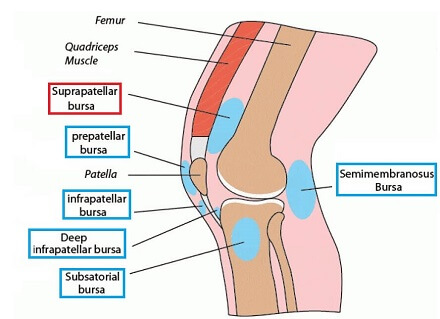
Bursae are small, fluid-filled sacs found throughout the body, especially in areas where friction between tendons, ligaments, muscles, and bones is common – think of them like tiny cushions.
There are a number of different bursa around the knee. The suprapatellar bursa is located just above the patella (kneecap) between the quadriceps tendon and the lower end of the femur (thigh bone).
The primary function of the suprapatellar bursa is to reduce friction and provide cushioning at the front of the knee joint and protect the surrounding structures from excessive wear and tear. During activities that involve lots of bending and straightening of the knee, e.g. walking, running, and jumping, the bursa allows the quads tendon to glide over the underlying bone, ensuring smooth joint movement.
With suprapatellar bursitis, aka quadriceps tendon bursitis, irritation of the bursa causes the synovial membrane (the lining of the bursa) to produce excess lubricating fluid to try and protect the knee. This causes the bursa to swell and become inflamed, resulting in suprapatellar bursitis.
What Causes Suprapatellar Bursitis?
Common causes of suprapatellar bursitis are:
- Repetitive Overuse: Repetitive activities that involve prolonged kneeling or squatting, such as gardening or certain occupations, or repetitive kicking or jumping e.g. certain sports, can irritate and inflame the suprapatellar bursa over time
- Direct Trauma: A sudden blow or impact to the front of the knee can lead to suprapatellar bursitis. This can occur during falls or sports-related injuries
- Infection: In some cases, the bursa may become infected, leading to a condition known as septic suprapatellar bursitis. This is a less common but potentially serious form of the condition
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of bursitis in various joints, including the suprapatellar bursa
- Quads Tightness: tightness in the quads muscles can cause the quads tendon to push down on and squash the suprapatellar bursa, placing it under greater pressure and making it more prone to friction
Suprapatellar Bursitis Symptoms
Common suprapatellar bursitis symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain above the knee is a hallmark symptom of suprapatellar bursitis. The pain typically worsens with knee movement, especially activities that involve bending the knee
- Swelling: Inflammation of the bursa can lead to a defined pocket of swelling just above the kneecap. The bulge tends to be soft to touch and can vary in size. The swelling is typically restricted to the bursa rather than causing general knee swelling
- Warmth and Redness: The affected area above the knee joint may feel warm to the touch and appear red or inflamed, particularly with septic bursitis
- Limited Mobility: Pain and swelling from suprapatellar bursitis can limit the range of motion in the knee joint, making it difficult to fully bend or extend the leg, and it may become painful to walk or go up and down stairs - check out our top tips for getting up and down stairs with knee pain
Suprapatellar Bursitis Diagnosis
In order to diagnose suprapatellar bursitis, your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, the onset of pain, any recent injuries or activities that may have contributed to the condition, and any underlying medical conditions.
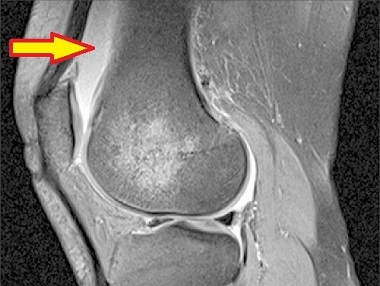
They will then carry out a physical examination, during which they will assess the knee joint, paying particular attention to the area above the patella. They may look for signs of swelling, warmth, redness, and tenderness.
In some cases, imaging studies may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of knee pain. These studies may include:
- X-rays: X-rays can help identify any abnormalities in the bones or joint structures.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging can visualize the bursa and assess for signs of inflammation or fluid accumulation.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI can provide detailed images of the soft tissues, including the bursa, and help determine the extent of inflammation.
In cases of suspected septic suprapatellar bursitis, your healthcare provider may perform an aspiration. This involves using a needle to withdraw a sample of fluid from the bursa for analysis, including testing for infection.
How Is Suprapatellar Bursitis Treated?
The treatment of suprapatellar bursitis aims to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain, and promote healing but may vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Suprapatellar bursitis treatment usually involves a combination of:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the affected knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, e.g. kneeling, squatting jumping and kicking, is the first step in suprapatellar bursitis treatment. Without appropriate rest, you keep irritating the bursa and slow down healing, similar to picking a scab
- Ice Treatment: Applying a cold compress or ice pack to the affected area can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Cold therapy is typically applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day
- Medications: Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen/Advil, can help reduce pain and inflammation from quadriceps tendon bursitis. If your doctor suspects a bacterial infection, such as septic arthritis, then you will be given a course of antibiotics
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy for suprapatellar bursitis usually includes a combination of electrotherapy treatment e.g. ultrasound or shortwave diathermy helps to reduce the inflammation in the bursa, and then working on a rehab program
- Exercises: Exercises are are a vital part of suprapatellar bursitis treatment usually consisting of a combination of knee strengthening and stretching exercises to improve the strength, stability and flexibility as well as reducing the pressure on the bursa. Specific exercises targeting quads strengthening and stretching exercises are particularly important, not only for reducing the symptoms of bursitis but also preventing recurrence
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation and pain, a corticosteroid injection may be administered directly into the bursa to reduce inflammation and reduce pain
- Aspiration: If there is significant swelling, then your healthcare provider may drain the excess fluid using a needle and syringe
- Surgery: Surgical intervention is rarely necessary for suprapatellar bursitis. However, in cases of chronic or recurrent bursitis that does not respond to conservative treatments, surgical removal of the bursa may be considered.
One of the key aims of suprapatellar bursitis is to reduce the swelling in the bursa, not only to reduce pain but also to reduce the risk of the excess fluid leaking out of the bursa and into the knee joint. There are lots of different options for knee swelling treatment that can help.
#CommissionsEarned from Amazon on qualifying purchases
Quadriceps Bursitis Recovery
Recovery time for suprapatellar bursitis will depend on a number of factors such as the severity of the condition, your overall health and how well you stick to your treatment and rehab program.
The earlier you start treatment, the quicker you are likely to recover as there is less irritation and inflammation of the bursa.
And it is really important to continue with your rehab program until you have regained full strength and flexibility in the knee muscles, otherwise the problem is likely to recur in the future.
Suprapatellar bursitis can take longer if there are other associated medical condition such as gout knee or arthritis. Mild cases of quadriceps tendon bursitis may settle down in a few weeks, whereas chronic cases can take 3-6 months to settle.
Prevention of Suprapatellar Bursitis
Preventing suprapatellar bursitis involves taking measures to reduce the risk of bursa irritation and inflammation. Here are some preventive strategies:
- Use Knee Pads: If you engage in activities that require kneeling or crawling, such as gardening or construction work, wear knee pads to cushion and protect the knees.
- Avoid Prolonged Kneeling: When possible, minimize prolonged periods of kneeling or squatting to reduce the risk of overuse and irritation of the suprapatellar bursa.
- Improve Technique: If you participate in sports or activities that involve impact or falls, learn and practice proper techniques to minimize the risk of knee injuries.
- Adequate Warm-Up: Prior to physical activities, engage in a thorough warm-up routine to prepare the muscles and joints for the demands of the activity.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy body weight can reduce excess stress on the knee joint and decrease the risk of bursitis.
What Else Could It Be?
There are a number of other bursa located around the knee which can also become irritated and inflamed causing localised pain and swelling:
- Prepatellar Bursitis: directly in front of the knee cap
- Infrapatellar Bursitis: just below the knee cap
- Pes Anserine Bursitis: on the inner side of the knee
- Semimembranosus Bursitis: at the back of the knee
There are also a number of other conditions that can cause pain and swelling above the knee, the most common being:
If you want some help working out what is causing your pain, visit the knee pain diagnosis section.
Summary
Suprapatellar bursitis is a common cause of swelling and pain above the knee.
Inflammation of the suprapatellar bursa is usually caused by a combination of muscle weakness, tightness and repetitive overuse, particularly sports involving lots of kicking and jumping.
Suprapatellar bursitis often causes a defined soft pocket of swelling above the knee which may be associated with tenderness, redness and warmth.
Treatment usually involves a combination of rest from aggravating activities, physical therapy, medications, and in some cases aspiration, corticosteroid injections or surgery.
Suprapatellar bursitis recovery may take anything from a few weeks to a few months depending on the underlying cause, severity and any associated conditions.
Page Last Updated: 06/02/24
Next Review Due: 06/02/26