- Home
- Knee Joint Anatomy
- Knee Muscles
- Quadriceps
- Vastus Lateralis
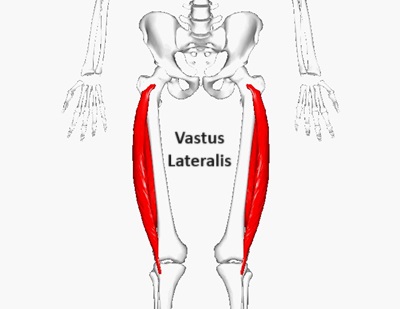
Vastus Lateralis Muscle
Written By: Chloe Wilson, BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed by: KPE Medical Review Board
Vastus lateralis, also known as vastus externus, is the largest and most powerful of the quadriceps muscles, found on the lateral (outer) side of the front of the thigh.
It works with the rest of the quadricep femoris to help straighten the knee and with activities such as getting up from a chair and going up and down stairs.
Tightness is the vastus lateralis muscle is a common cause of outer knee pain as it pulls the kneecap slightly out of position resulting in friction and irritation when the knee moves.
Vastus Lateralis Origin & Insertion
Vastus lateralis originates from various parts of the femur (thigh bone) over a large area:
- upper lateral part intertrochanteric line
- lower border greater trochanter
- lateral side gluteal tuberosity
- upper half lateral lip of linea aspera
- lateral intermuscular septum
These parts blend together to form a broad, flat tendon (known as an aponeurosis) that runs downwards and forwards to the knee joint, quadriceps femoris tendon.
The main muscle bulk of vastus lateralis is found on the upper half of the lateral side of the thigh. It then forms a broad tendon which narrows as it approaches the patella (kneecap).
Here, the vastus lateralis tendon inserts into one of the other quadriceps tendons (rectus femoris) and the outer side of the patella. Some fibres blend with the iliotibial band (ITB) which, to a large extent, replaces the local part of the joint capsule and then attaches to the tibial tuberosity, just below the patella.
Function Of Vastus Lateralis
Vastus lateralis works with the other quadriceps muscles to extend the knee, particularly with activities such as getting up from a chair, climbing stairs and cycling.
It is also the recommended site for intramuscular injections in infants under seven months old and in those with loss of muscle tone, usually due to not being able to walk.
Tightness in vastus lateralis and resultant lateral retinaculum tightness can cause the patella to shift or tilt which can cause problems with patella tracking and increase the risk of patellar dislocation. This tightness can be treated with stretching exercises or lateral release knee surgery.
Common Problems
The most common knee problems associated with vastus lateralis issues are:
- Muscle Tightness: tightness in vastus lateralis pulls the kneecap sideways which affects how it glides up and down, resulting in knee cap pain.
- Muscle Strain: over-stretching or over-loading of the muscle causes tearing in the muscle fibres and quads strain
- Contusion: a blow to the side of the leg causing bruising in the muscle
- Kneecap Instability: there is an increased risk of kneecap dislocation if the muscle is tight
Vastus lateralis muscle imbalance is often linked with:
If you have knee pain due to vastus lateralis problems you may be interested in:
- Quads Strengthening Exercises: Loads of great ways to strengthen vastus lateralis and the other quads muscles
- Quads Stretches: Simple test to see if your quads are tight and some great knee stretching exercises you can do at home
- Knee Muscles: Find out about the other muscles around the knee, how they fit together and how they work
- Common Knee Problems: Find out all about the most common things that go wrong in the knee and how to fix them
Vastus Lateralis Summary
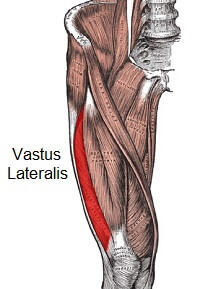
Name: Vastus lateralis or vastus externus, part of quadriceps femoris
Action: Knee extension (straightening)
Origin: Several areas of the femur – upper lateral part intertrochanteric line, lower border greater trochanter, lateral side gluteal tuberosity, upper half lateral lip of linea aspera, lateral intermuscular septum
Insertion: Rectus femoris tendon and lateral border of the patella
Functional Activities: Sit to stand, stairs and squats
Nerve Supply: Muscular branch femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4)
Blood Supply: Lateral Circumflex Femoral Artery
Other Knee Muscles
Related Articles
Last Updated: February 3rd, 2026
Next Review Due: February 3rd, 2028